The Different Types of Hearing Loss – A Comprehensive Guide
Hearing shapes our connection with the world, allowing us to engage with our surroundings in meaningful ways and cherish the sounds that life has to offer. The ability to listen to a loved one’s voice, relish the melodies of music, or even detect potential dangers all hinge on this delicate sense. When hearing becomes compromised, it doesn’t simply affect one’s ability to perceive sound – it can lead to a profound sense of isolation, affecting personal relationships and overall well-being.
This comprehensive guide will take you through the three primary types of hearing loss so you can recognize the signs, understand the implications, and explore the available solutions. With the right information and support, finding clarity in a world that has grown quiet is more than just a possibility – it’s a promise.
The Silent Struggle & Impact of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can subtly alter daily existence before a person even notices. Simple conversations become straining, and misunderstanding others in social settings may lead to retreating from social life. Productivity at work can suffer due to muffled hearing, and enjoying music or television might require higher volumes and affect relationships at home.
In the United States, about 15% of adults report some trouble hearing. Amongst them, those who face difficulties often experience higher levels of stress and anxiety due to the constant challenges in communication. Particularly concerning is the impact on older adults, as hearing loss is the third most common chronic condition faced by this group and can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and depression.
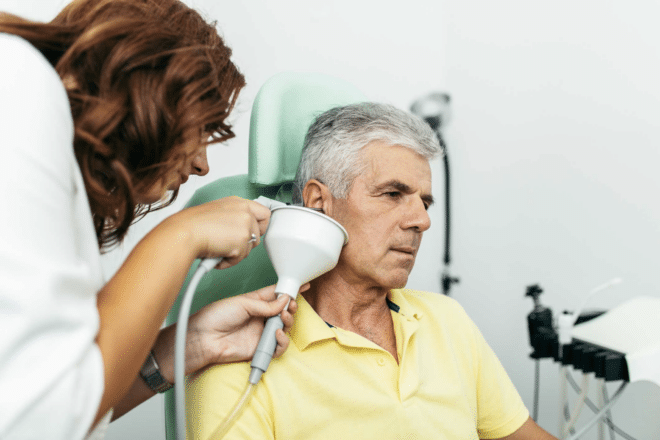
If you’ve noticed changes in your hearing, taking the first step toward addressing your hearing health and determining the specific type of hearing loss through an accurate diagnosis is essential.
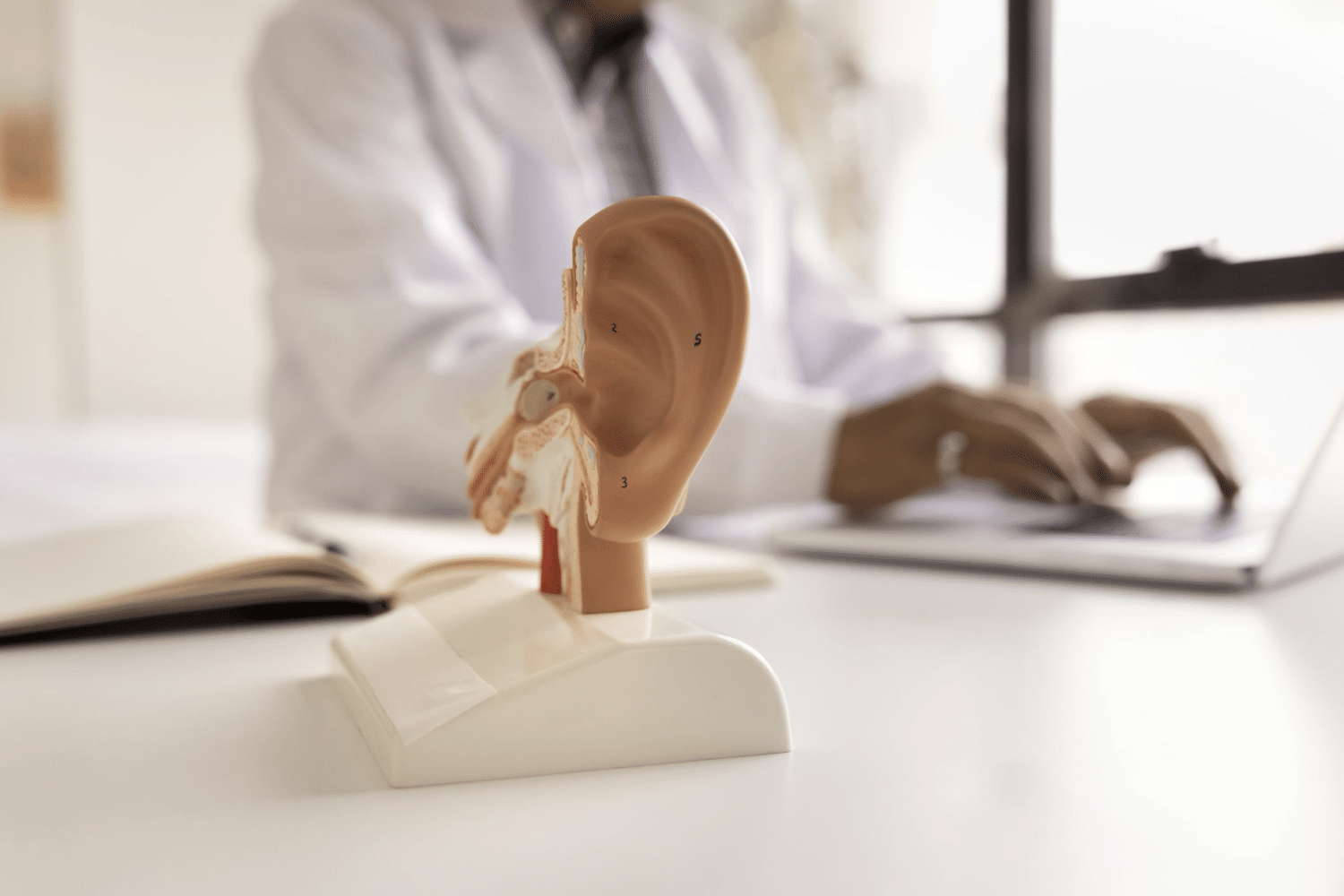
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound waves are hindered within the ear’s outer or middle sections. This blockage prevents the full spectrum of sound from reaching the inner ear, leading to diminished hearing. This type of hearing loss is often treatable, and a thorough evaluation can determine the proper course of action to restore the affected individual’s hearing capabilities to their fullest potential.
The Root Causes of Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss can result from various factors. Ear infections can cause inflammation and fluid buildup that disrupt sound transmission. Earwax accumulation creates a physical barrier that can impede sound passage. Permanent conditions like benign tumors exert pressure and impair auditory function. Structural anomalies or congenital disabilities, such as a perforated eardrum or dislocated ossicles, may also hinder hearing. Foreign objects in the ear and allergic reactions can result in swelling and directly impact hearing health.
The Signs & Symptoms of Conductive Hearing Loss
Individuals with conductive hearing loss may experience a sudden decrease in hearing, pressure or pain sensations in the ear, or ongoing fluid drainage from the ear. There may also be issues with balance if the inner ear is affected.
Treatments for Conductive Hearing Loss
Effective treatment for conductive hearing loss varies, often involving medical intervention, such as removing earwax or treating infections with medication. In cases of structural issues, surgical procedures may be necessary. For those not suitable for surgery, hearing aids with a specialist’s precise calibration can significantly improve auditory function.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing loss. It happens when there’s damage to the inner ear or the nerve pathways from the inner ear to the brain. This damage can mean that even when sound is loud enough and clear, it may still be hard to understand or sound muffled.
The Root Causes of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sound enters our ears, but it’s the delicate inner ear structures that truly interpret these waves. Sensorineural hearing loss emerges from damage to these inner ear cells or to the nerve pathways leading to the brain. Causes can range from aging and loud noise exposure to head trauma and even genetic factors. Some infections or drugs can be harmful to these sensitive cells and result in hearing challenges. Meniere’s disease, characterized by symptoms like vertigo and tinnitus, can also lead to sensorineural hearing loss.
The Symptoms and Signs of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
People with sensorineural hearing loss often find it hard to follow conversations, especially with background noise. They may notice a ringing in their ears, called tinnitus, or feel that sounds seem quieter than usual or lack clarity. Some even experience dizziness along with hearing issues.
Treatments for Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Unfortunately, sensorineural hearing loss is often permanent. However, hearing aids and assistive listening devices can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with this type of hearing loss. Cochlear implants may be recommended in certain cases, particularly for individuals with severe to profound hearing loss.
Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed hearing loss is when a person has both conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss at the same time. This means there are issues with how sound is carried in the outer or middle ear and also problems with how the inner ear or hearing nerve works. It can make hearing a more complex challenge to address, as there are multiple factors that affect a person’s ability to hear clearly.
The Root Causes of Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed hearing loss combines problems in the outer or middle ear and the inner ear or auditory nerve. People with this kind of hearing loss may struggle because of ear infections or bone growths in the outer ear and damaged inner ear cells or nerve pathways. Age, working in noisy environments, head injuries, and certain medical conditions can also lead to these hearing problems.
The Signs and Symptoms of Mixed Hearing Loss
People with mixed hearing loss often notice that sounds are both quieter and less clear. They might say it’s hard to understand what others are saying, especially when there’s a lot of noise around, like in a crowded room. Some other signs might include a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ears, or they might suffer from tinnitus. It might also be tougher to figure out where sounds are coming from.
Treatment Options for Mixed Hearing Loss
Treatment options for mixed hearing loss involve addressing both the conductive and sensorineural components. Management may include surgery, medication, or both, alongside fitting hearing aids or considering cochlear implants to enhance sound perception and improve communication.
Seek Treatment at Hearing Health Connection
Don’t let misinformation or fear prevent you from reaching out for the support you need. Seeking professional help for hearing loss is the first step towards reclaiming your auditory independence. If you have any degree of hearing loss, our expert audiologists at Hearing Health Connection are equipped to diagnose and tailor interventions for you. Book a hearing evaluation at one of our Pennsylvania hearing care centers and begin your path to better hearing today.